Successful implementation of a self-service portal
With a self-service portal, employees can complete many user management tasks themselves. User self-service is becoming more and more prevalent for a simple reason: Companies save time. But only if the user self-service is properly integrated. To do this, you need to consider various steps and requirements.
Index
Employees help themselves
Definition self-service portal
A self-service portal is a website that consists of self-service and self-help functions. An identity self-service portal is particularly well suited for simplified identity management. Employees can use it to
- manage their digital identity themselves,
- correct their own personal data,
- request services,
- find information
- and more.
In principle, all employees of a company can use the portal. Depending on how a company is organized, departments and user groups are assigned different tasks. In addition, they are given different permissions that allow them to edit data, for example.
In addition, employees can access information about colleagues, departments and important contact data. Ultimately, it varies from company to company what the self-service portal can do.
Advantages of a self-service portal
A self-service portal offers advantages, both for the employee and for the IT department. If the IT department can delegate routine tasks, it receives fewer calls and tickets. The time savings benefit not only the IT department, but the entire organization.
Employees often know best what information is up-to-date or required. Whether it’s a new phone number, or an expired password – without a self-service solution, the employee must adjust to long processes for even the smallest changes. If the user decides to pass the problem on to the HR department, the requests are often collected. Only after a time delay do they get passed on to IT.
With a self-service solution, you can
- shorten processes and save time: Administrative processes cost time and lead to long waiting times. In the worst case, the employee has to wait several hours or even days for a request for access rights to a project. During this time, the colleague may not be able to work.
- increase data quality: If every user can immediately and effortlessly update their data, the organization’s data quality will correspondingly increase and always be up-to-date.
- reduce costs: Faster processes, hardly any waiting times and fewer tickets have the effect of minimizing costs.
Most important features
In a self-service portal, very simple to very complex tasks can be completed. According to our experience, most companies use self-service functions to
- search for information,
- update data (for yourself, for colleagues),
- request access rights to drives or projects (group management),
- as well as reset passwords.
However, the possibilities are manifold and depend on the organizational structure of the company.
When selecting a self-service portal, you need to pay attention to more than just the features. Other criteria must be met without fail:
- User friendliness: Is the software easy to use and does it add value as perceived by users? Since every employee should use it, you need an intuitive, easy-to-use tool. Everything from the login to the design must be user-friendly.
- Security: How do you want to use the self-service solution? Who should have access to what? The issue of data security plays an essential role.
- Data source: Should the portal access Active Directory (OnPrem), a cloud directory (Microsoft 365, Cloud Identity), or both?
- Deployment: How should the self-service be hosted?
- Report and log: Which data should be registered, which should be evaluated regularly? Every change has a direct impact on the directory. It is therefore important that the IT department has a log available. This can also be used to create reports in order to track and improve the use of the portal.
Read more about the advantages and features in our article “Self Service – Effektives IAM mit der FirstAttribute AG”.
Self-service concept
For your self-service portal, it is best to start with a well thought-out concept. You should take the time to clarify the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the portal and what do we want to achieve with it?
- Should it primarily be a portal for updating personal data and resetting passwords?
- Should it be included in a phone book?
- Who gets access to which information?
- Who should be allowed to read and/or write about what?
- Should approval workflows be built in?
- Which requests should be managed with it?
- Who monitors the access?
- What are the risks and how can we eliminate them?
This is an important step not only for IT, but also for the rest of the company. A role and permissions concept takes all essential factors into account in advance so that the self-service portal ultimately meets all the requirements.
Controlled access – Employee vs. manager self-service
In a typical IAM self-service, you don’t want all users to have the same rights. That’s why you need different “roles“. Each employee belongs to one or more roles. For each role it is defined: “Who is allowed to see, update, request and approve what.”
Two main roles can often be defined:
- the employee self-service role and
- the manager self-service role.
The employee self-service has access to restricted data only. This role is not allowed to see everything, possibly only update specific fields or request certain permissions.
In contrast, the manager self-service role has more rights. It can approve requests from employees, is allowed to edit more and retrieve more information.
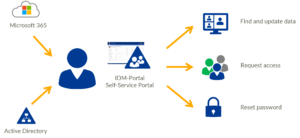
IDM-Portal self-service
FirstWare IDM-Portal is a self-service portal for end users. Its advantage is the easy handling, which does not require any in-depth IT knowledge.
With IDM-Portal, employees maintain and manage their personal data themselves. They request access rights and reset passwords themselves.
The authorizations are bound to different roles. Employees, groups, departments, locations get different rights and can thus assume responsibility.
The role and permissions concept provides an additional layer of security. It supports compliance with the access rules and policies that apply to the entire company.
IDM-Portal offers a wide range of self-service options:
- Information self-service
- Profile self-service
- Permission self-service
- Password reset self-service
- Project self-service
- Self onboarding
With IDM-Portal, you can delegate your user management securely and controlled to non-IT staff. For this purpose, the portal is directly connected to your Active Directory and/or Microsoft 365/Entra ID.